
Before taking a flight from Burgas, Bulgaria, I spent a few hours exploring one of the best aviation museums I have ever visited, Aviomuseum Burgas. Located at the entrance to Burgas Airport (BOJ), it is very easy to find.
Opened in 2017, the museum charges an entrance fee of only 6 LV (2€ or $3.35). The exhibits include Bulgarian civil and military aircraft from 1960 to 1996, such as an AN-12 transport aircraft, a TU-154 airliner, and many more that I will cover in this article.
Aviomuseum Burgas: What I Found?
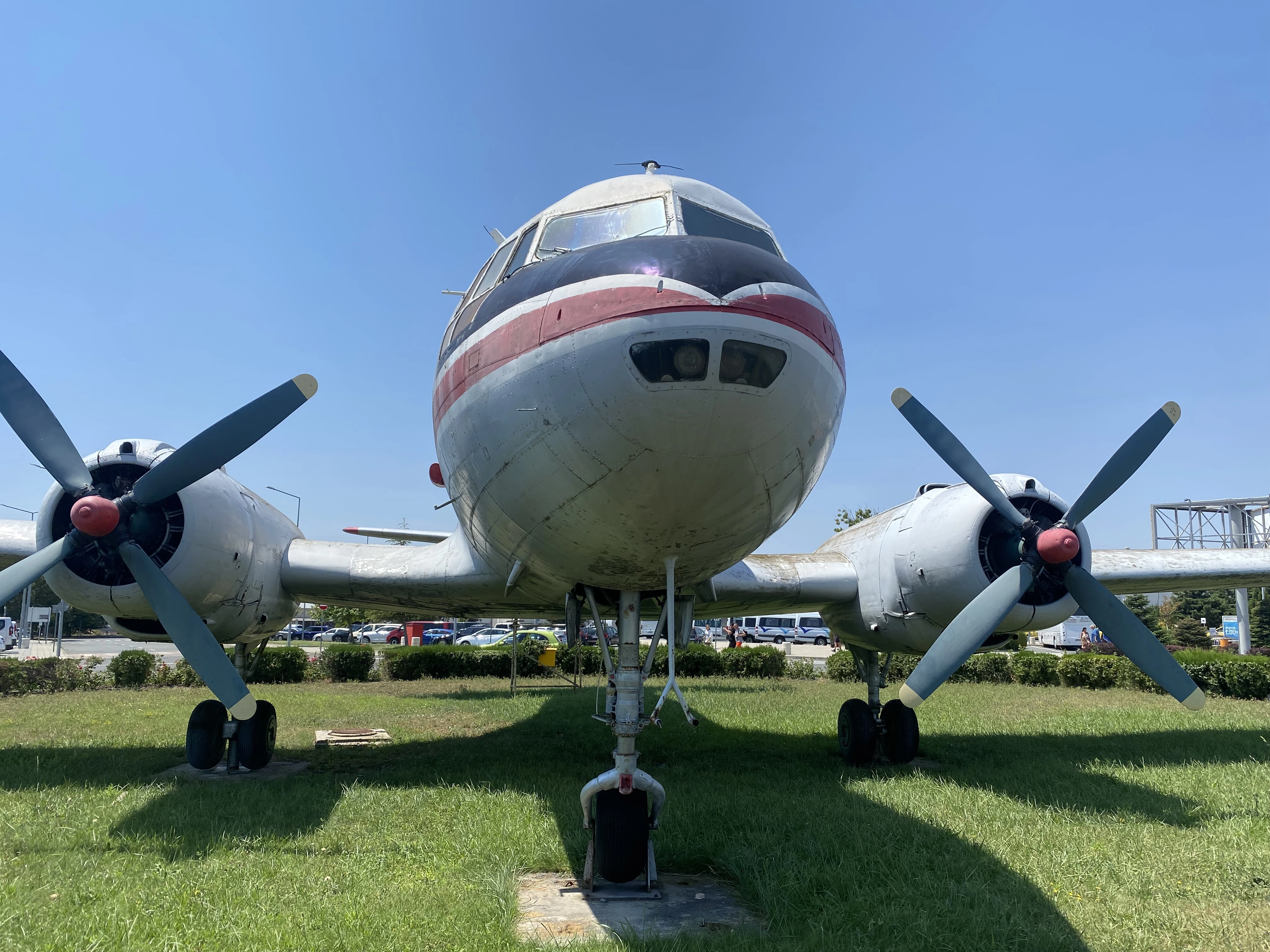
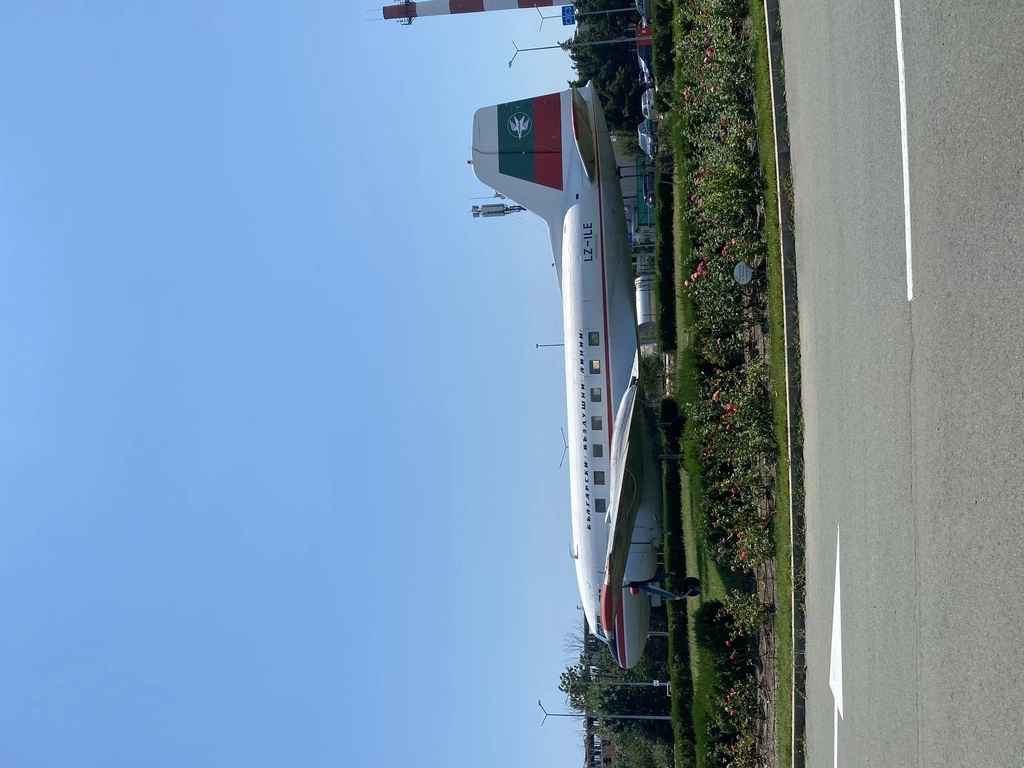
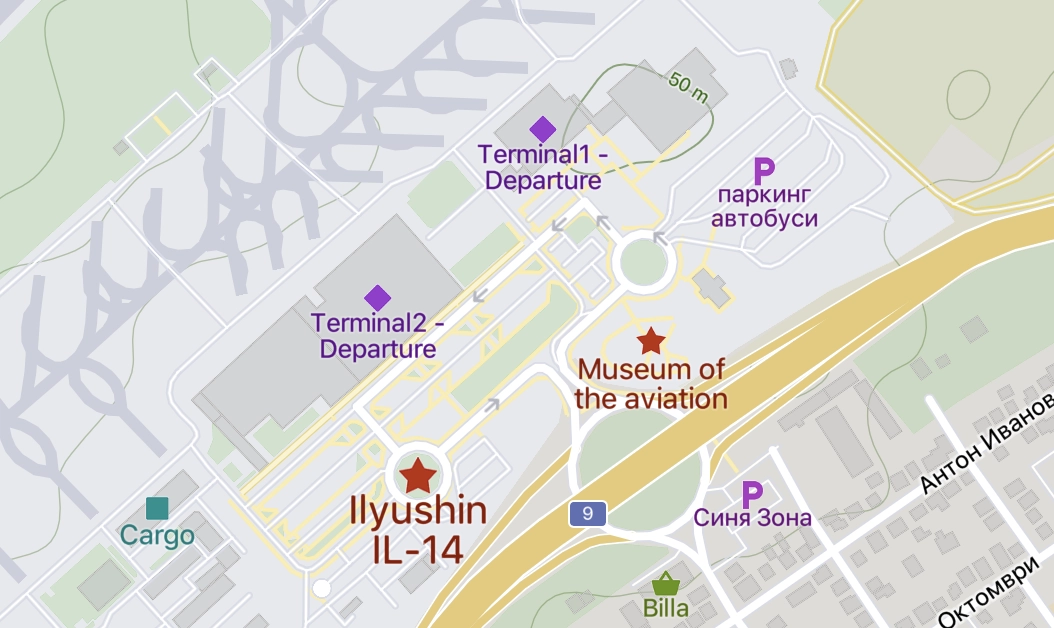
I discovered the following aircraft: Tu-154, An-12, An-24, MiG-17, MiG-21, L-29, An-2, An-14, Ka-26, and Mi-2. Although not part of the museum, about 100 meters away, an entire IL-14 aircraft sits on a roundabout at the airport entrance.

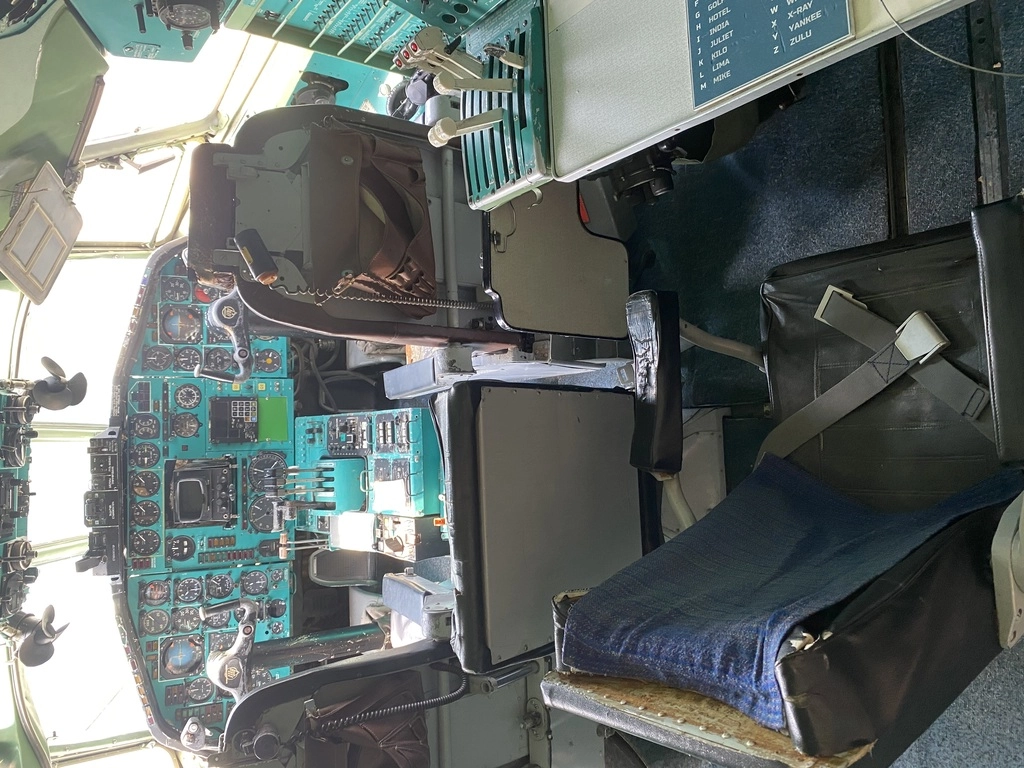
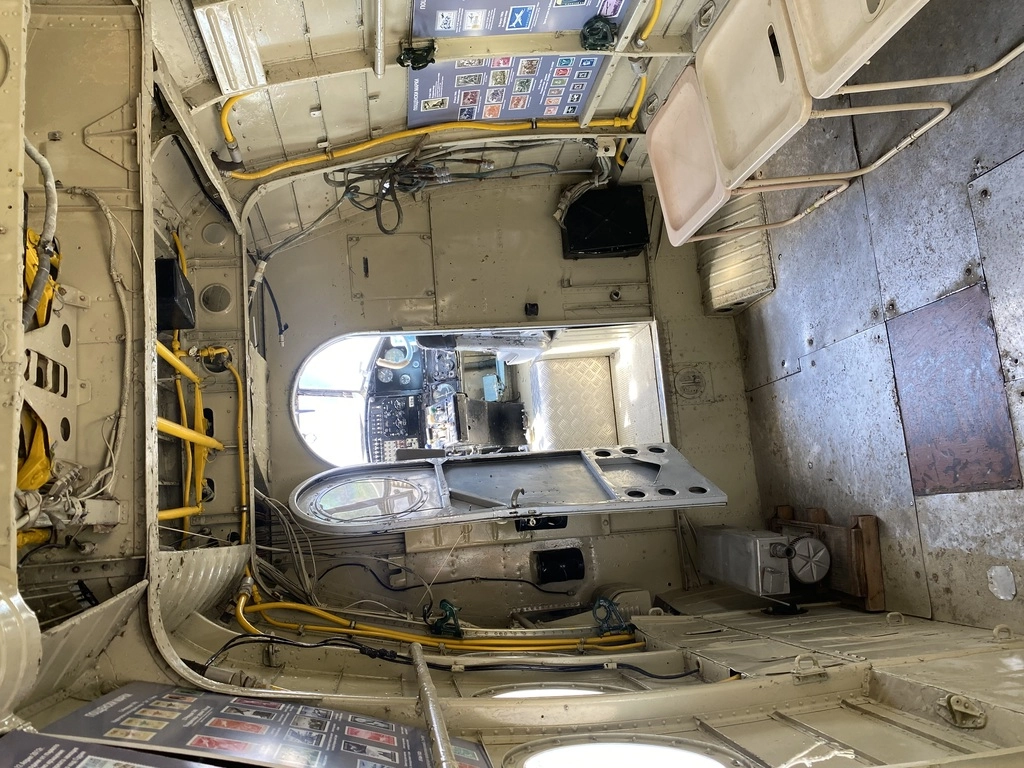
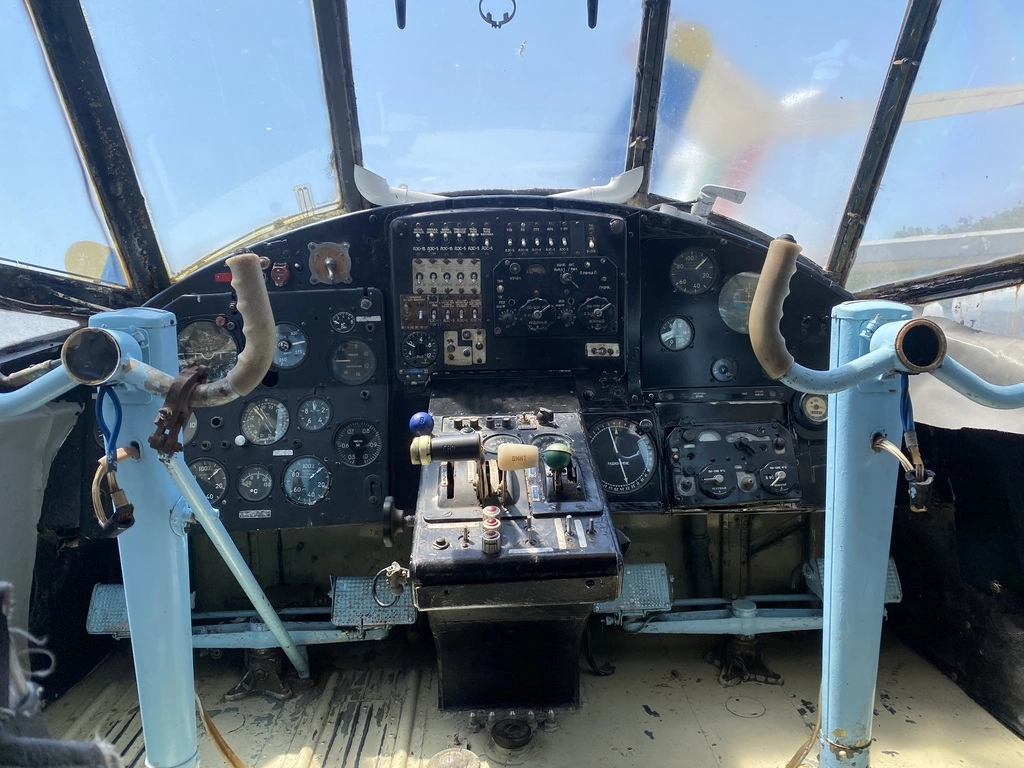
Visitors also have the unique opportunity to climb into the cockpits of several aircraft, including the MiG-17, MiG-21, Tu-154, and An-2.
The impressive interactive exhibit, Homo Volans (The Flying Man), is in an An-12 aircraft. This exhibit features numerous authentic items, airplane models, costumes, installations, and archives from aviation history.
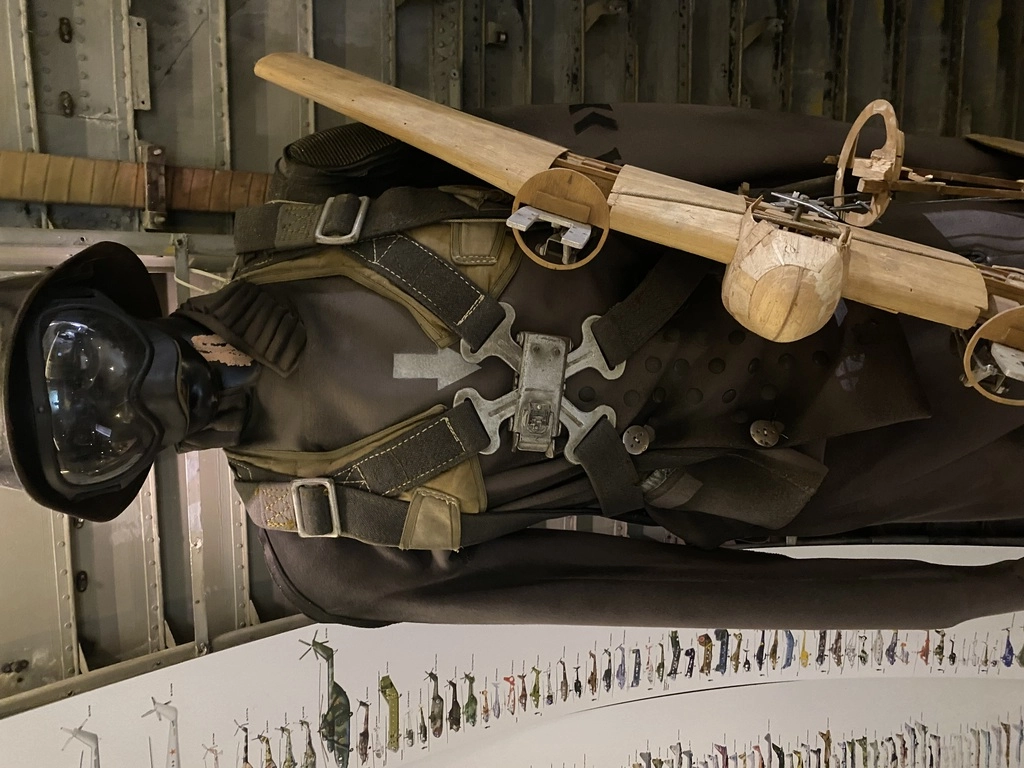
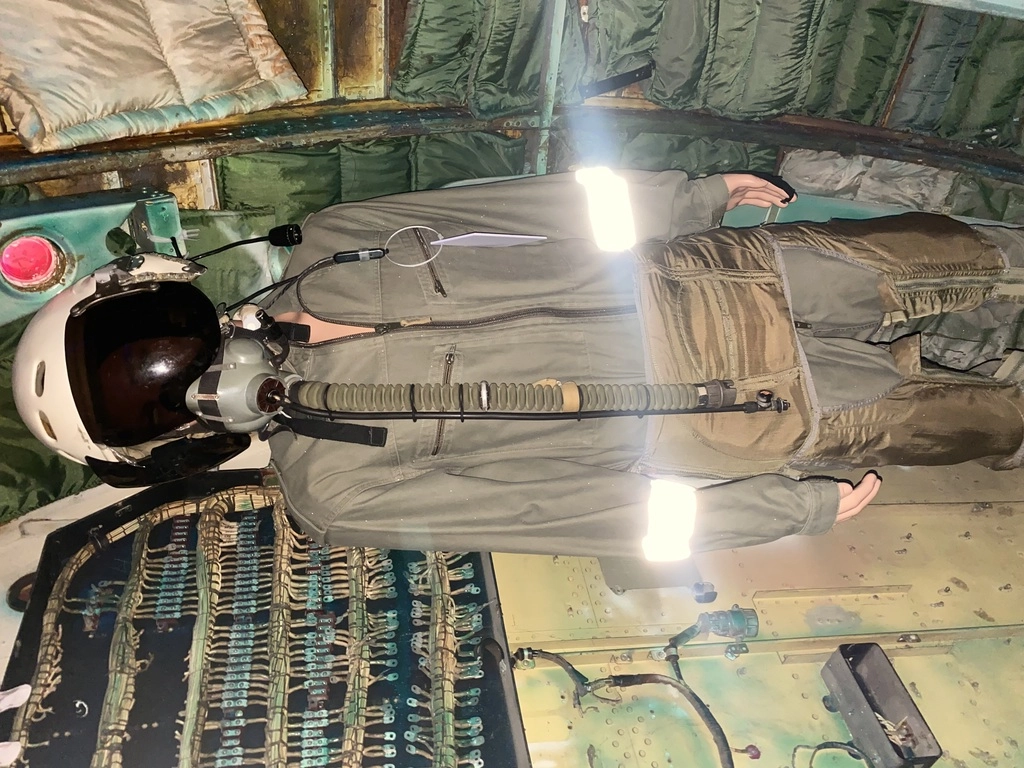


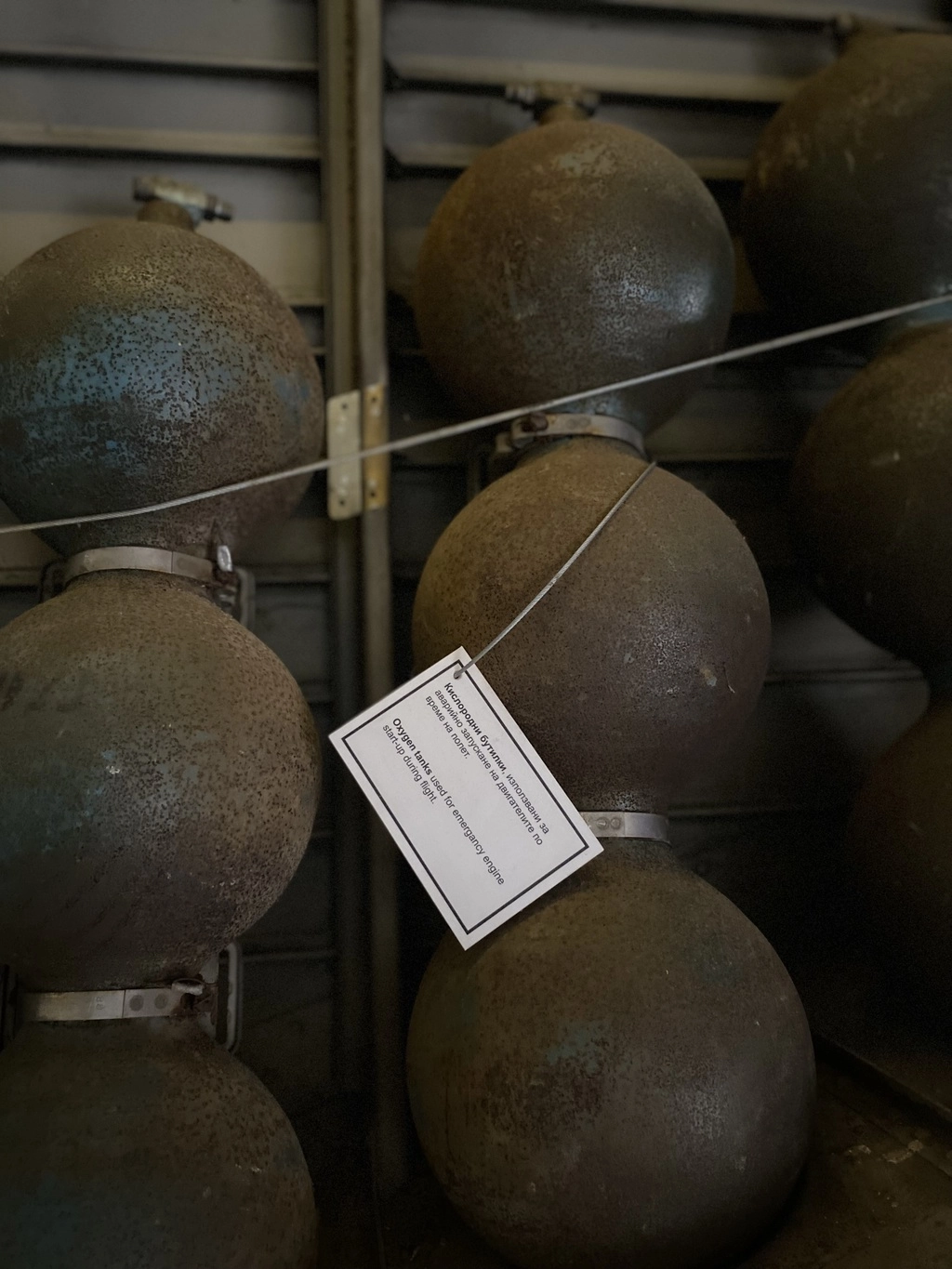
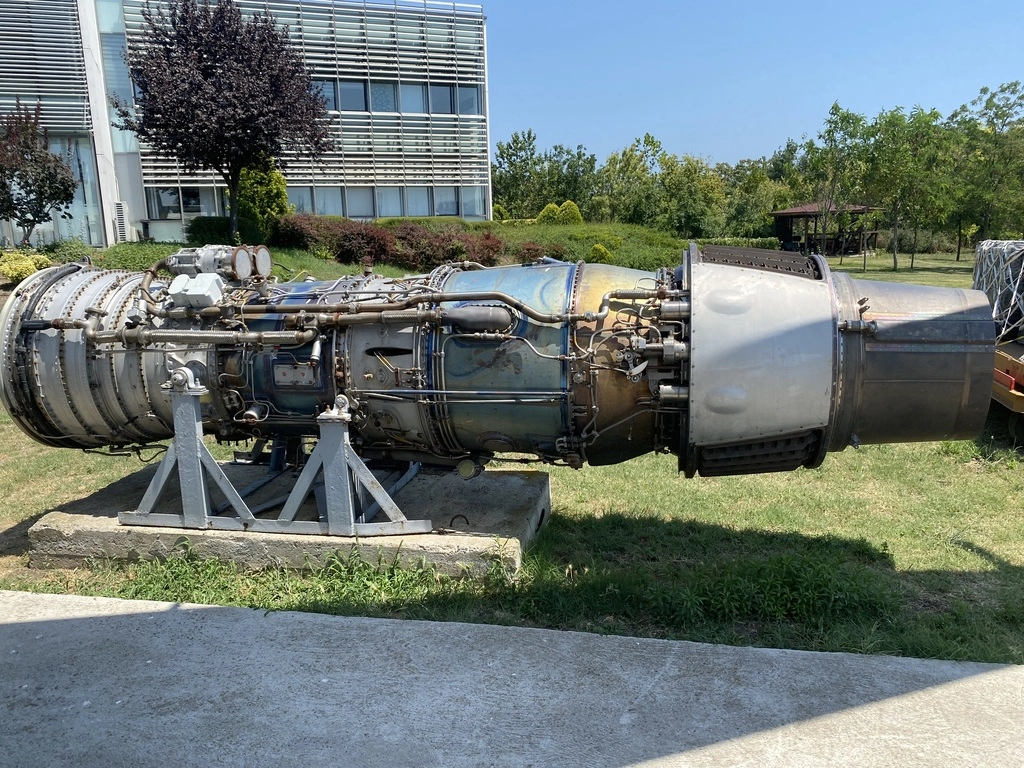
Some things that caught my attention included a black box, which could record up to 8 hours of data, oxygen tanks shaped like hyotan (Japanese sake bottles), and a Tu-134 engine (outside near An-12).



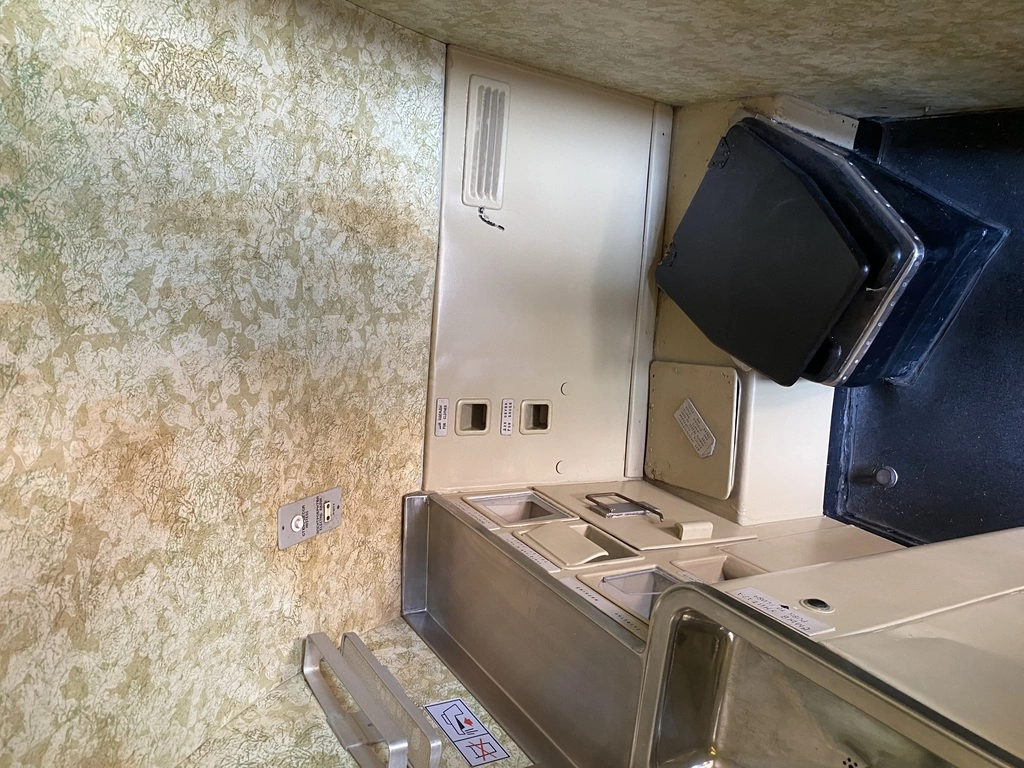
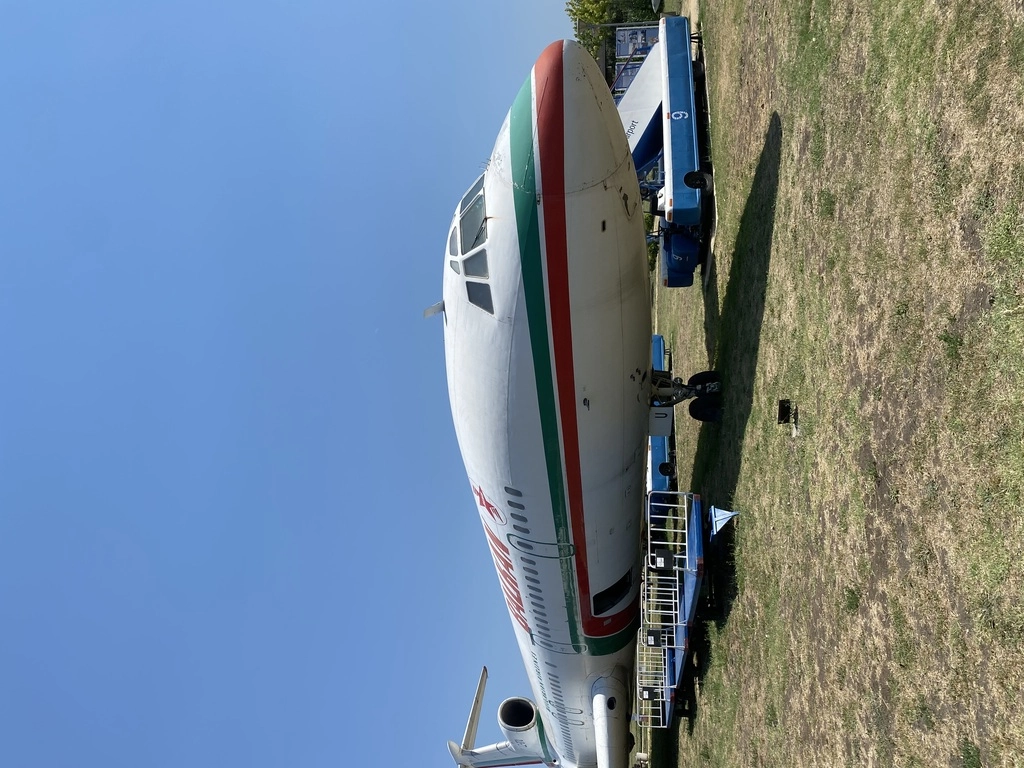
The Tu-154 airliner has been restored to reflect the 1970s style of Balkan Bulgarian Airlines. It was fascinating to see the ample space in the economy section, which was quite unusual compared to modern aircraft.
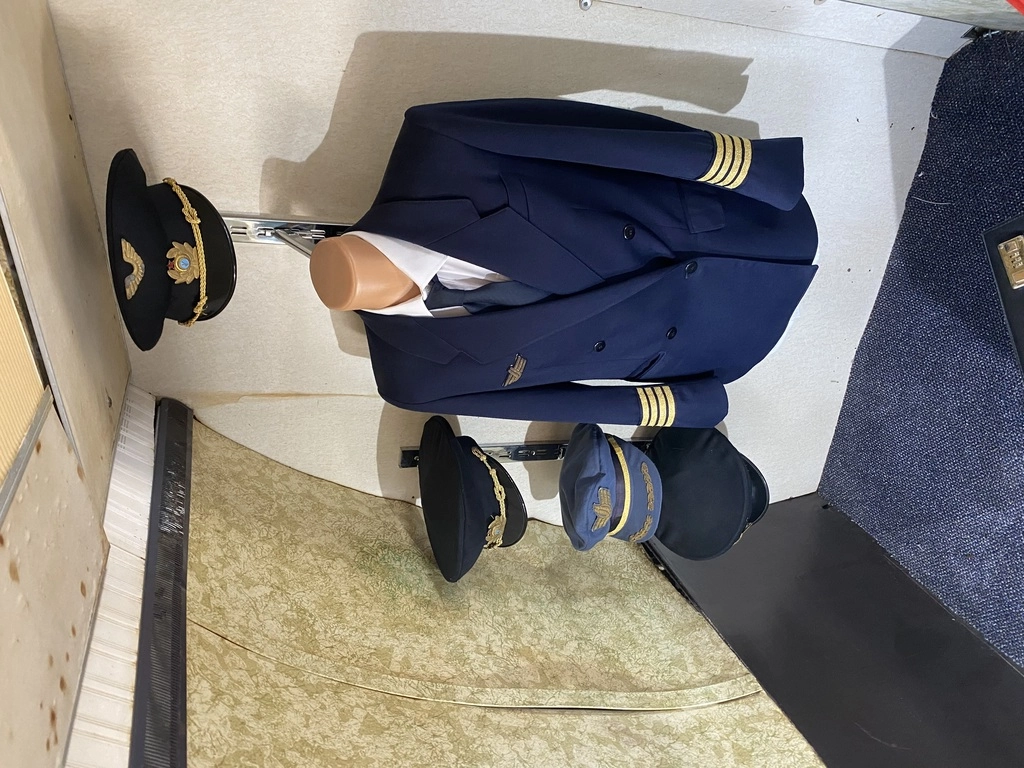



The museum’s goals extend beyond preserving these aircraft for future generations. They aim to develop the site as a center for learning about aviation technology, and highlighting the importance of Bulgarian civil aviation.
I really enjoyed my time there, as it was not only interesting to see the old aircraft and their designs, but also fascinating to witness so many man-made machines that have revolutionized the way we travel today.
Now, I would like to share with you the history and performance details of each aircraft below.
Tupolev TU-154
The TU-154, specifically the Tu-154B-2 variant, entered the Civil Force Registry in April 1981 under the Balkan Bulgarian Airlines. It was used to transport the passengers, with its inaugural flight being to the city of Manchester, England. From June 1992 to June 1994, this aircraft operated under the Macedonian flag.
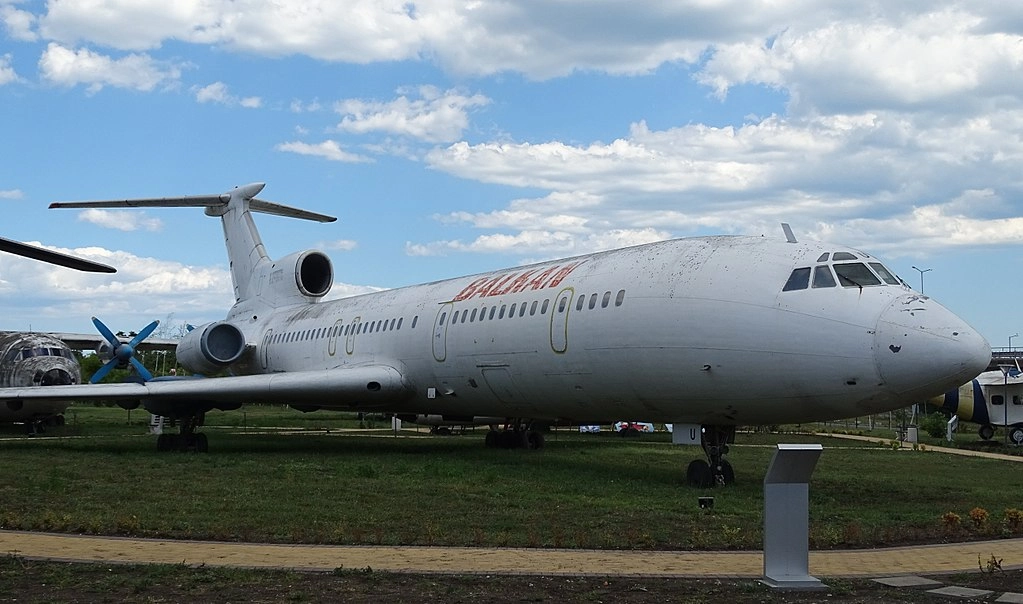
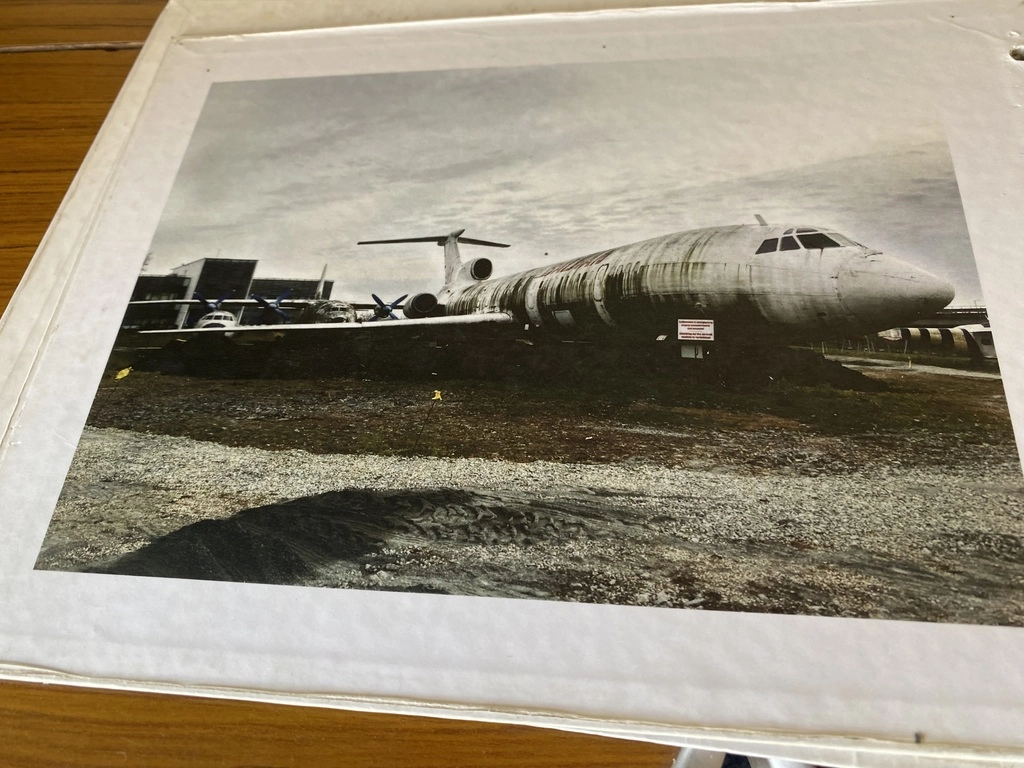


The Tu-154B-2 made its final landing on October 31, 1996, at Burgas Airport, concluding its 15 years of service with the Bulgarian Civil Aviation.
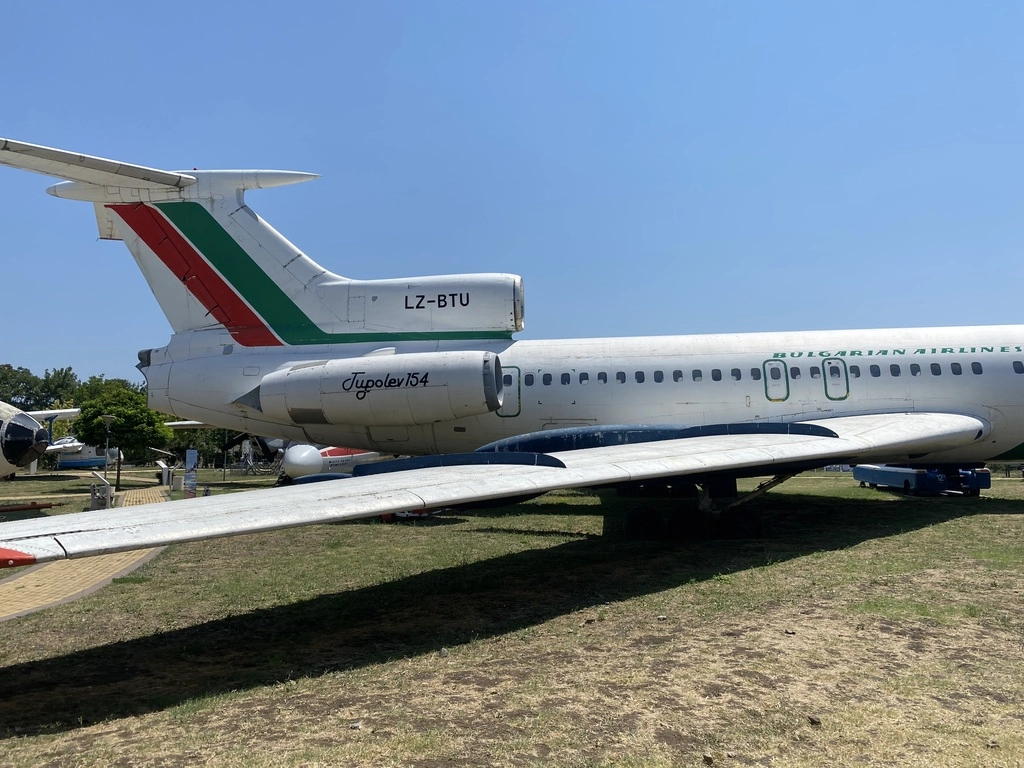

The TU-154 had its first flight on October 3, 1968, and a total of 1,026 units were built. The aircraft typically operated with a crew of four, including a captain, first officer, flight engineer, and navigator. It had a passenger capacity ranging from 164 to 180. As of today, there are 40 TU-154 aircraft still in operation, with the Russian Air Force flying the majority, totaling 19 planes.

| TU-154B-2 Specifications | Description |
|---|---|
| Length | 157 ft 1 in (47.90 m) |
| Wingspan | 123 ft 2 in (37.55 m) |
| Height | 37 ft 5 in (11.40 m) |
| Empty Weight | 111,800 lb (50,700 kg) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 220,000 lb (100,000 kg) |
| Engines | 3 x Kuznetsov NK-8-2U |
| Engine Power | 3 x 10,500 hp |
| Cruise Speed | 559 mph (900 km/h) |
| Range with Max Fuel | 2,100 nmi (3,900 km) |
| Service Ceiling | 39,700 ft (12,100 m) |

Antonov AN-2
The AN-2, specifically the AN-2P variant, was manufactured in 1970 and delivered to Bulgaria in January 1971. It was used for aerochemical operations, crop dusting, cargo services, and more.
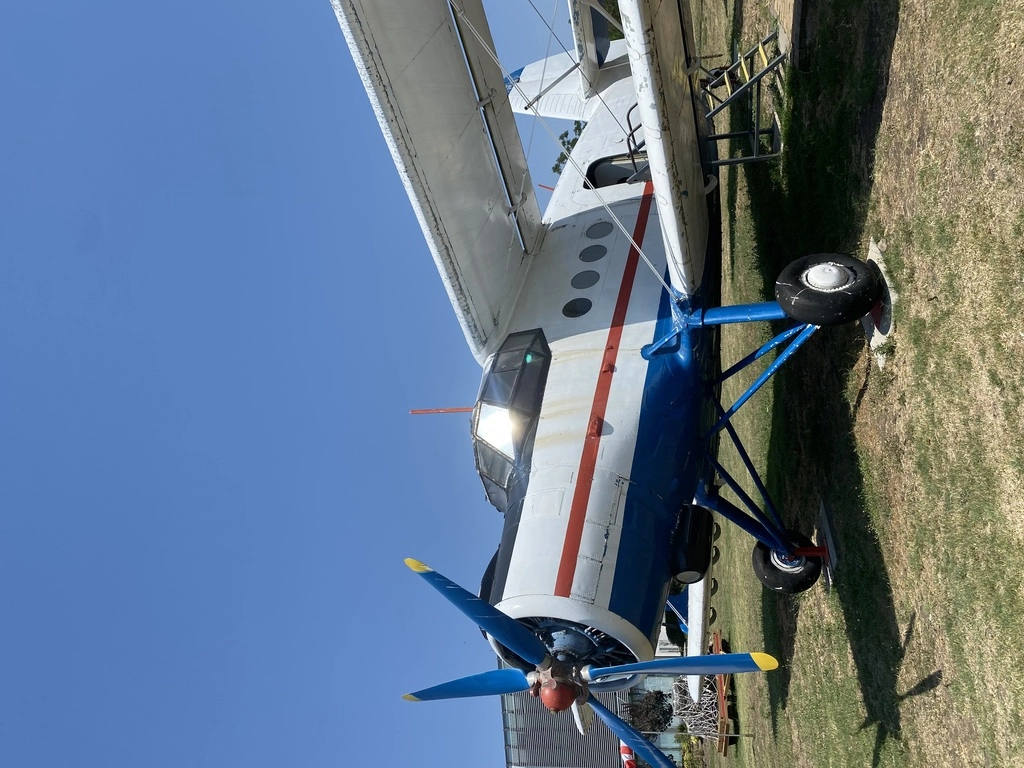

The aircraft’s last flight took place in May 1989, and it was officially retired in November 1992 after reaching a total of 11,354 flight hours, nearing its limit of 12,000 hours. The AN-2 served in Bulgaria for 19 years.

A total of 18,000 AN-2 were built. Its first flight was on August 31, 1947. The aircraft had a crew of 1-2 and could carry 12 passengers. Some AN-2s are still in operation today, though the exact number is unclear, estimated to be less than 10.

| AN-2 Specifications | Description |
|---|---|
| Length | 40 ft 8 in (12.4 m) |
| Wingspan | Upper - 59 ft 9 in (18.2 m)Lower - 46 ft 7 in (14.2 m) |
| Height | 13 ft 5 in (4.1 m) |
| Empty Weight | 7,275 lb (3,300 kg) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 12,125 lb (5,500 kg) |
| Engines | 1 x Shvetsov ASh-62 |
| Engine Power | 1,000 hp |
| Cruise Speed | 120 mph (190 km/h) |
| Range | 456 nmi (845 km) |
| Service Ceiling | 14,800 ft (4,500 m) |
Antonov-14
The An-14 was produced in 1970 with the intention of replacing the An-2 but ultimately proved to be less successful. The registration of this An-14 in the Civil Force Registry occurred in January 1971, and it was assigned to Ravnets Air Base (demolished and closed in 2000).
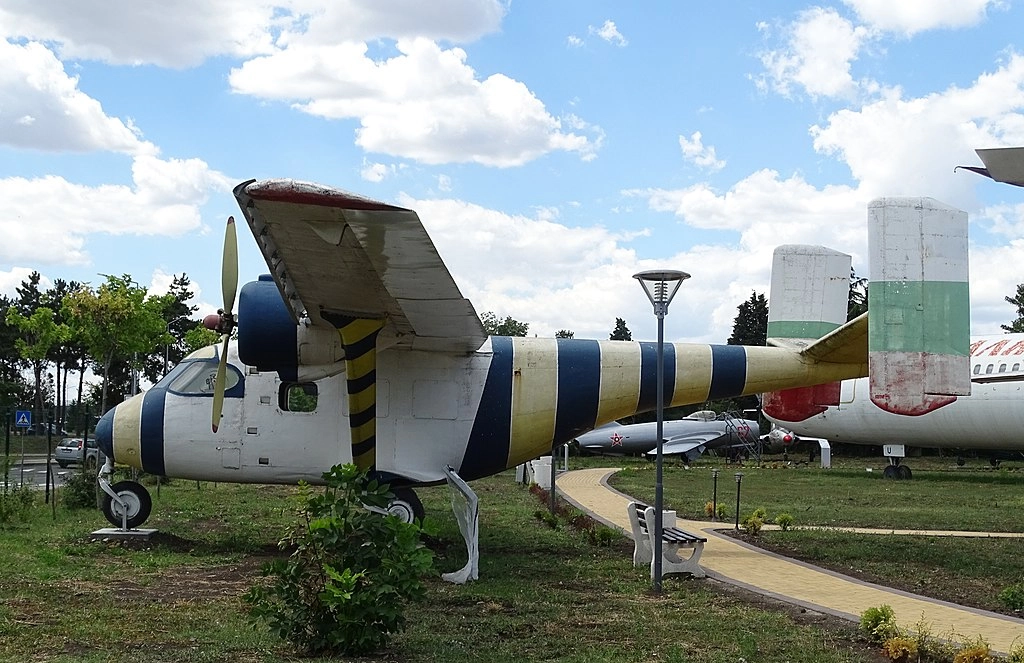

The An-14 is an easy to fly aircraft, making it suitable for pilots with only a few hours of training. It was used for a variety of tasks including aerial photography, monitoring for drownings and spills, and fish passages until 1985. The aircraft served in Bulgarian agricultural aviation for 14 years. The Antonov An-28 succeeded the An-14.
A total of 332 units of the An-14 were built. Its first flight took place on March 29, 1958. The aircraft has a crew of two and can carry 6 to 8 passengers. However, it is unclear how many of these types are still in operation.

Interestingly 2 of An-14 can be found in Kaunas, Lithuania. One in S. Darius and S. Girėnas Airport (EYKS) and another in Gamykla Heliport (EYKG).
| AN-14 Specifications | Description |
|---|---|
| Length | 37 ft 3 in (11.36 m) |
| Wingspan | 72 ft 2 in (21.99 m) |
| Height | 15 ft 2 in (4.63 m) |
| Empty Weight | 5,732 lb (2,600 kg) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 7,937 lb (3,600 kg) |
| Engines | 2 x Ivchenko AI-14RF |
| Engine Power | 300 hp |
| Cruise Speed | 110 mph (180 km/h) |
| Range | 300 nmi (650 km) |
| Service Ceiling | 16,000 ft (5,000 m) |
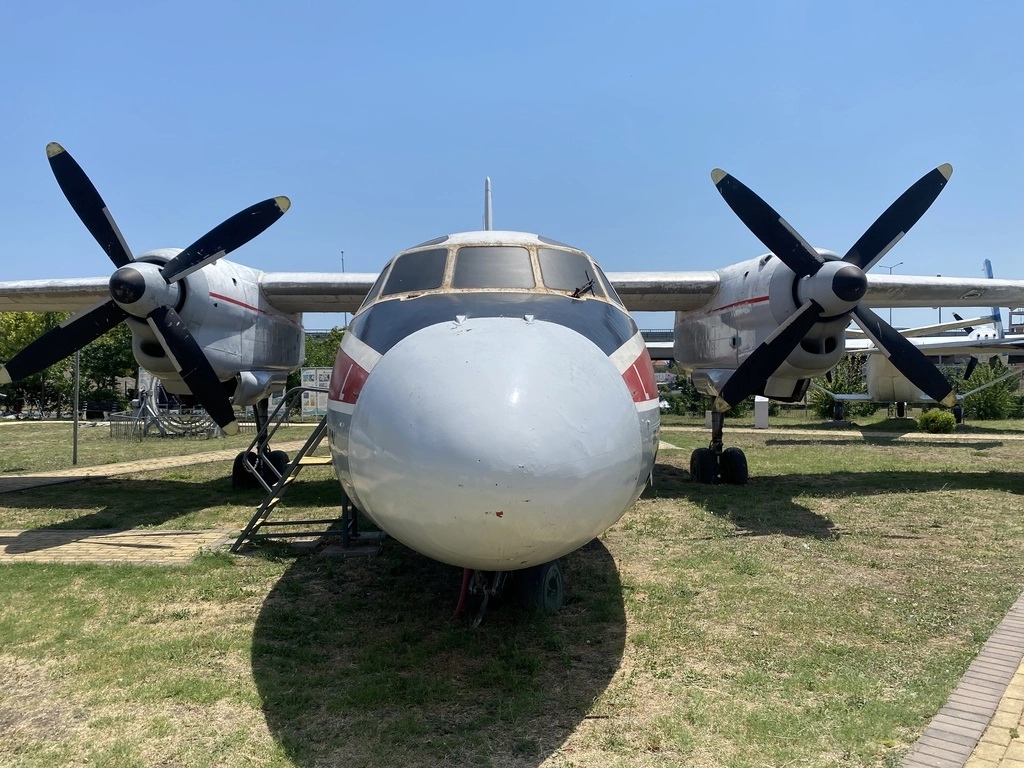
Antonov-12
The An-12 was produced and registered in 1968 by the agricultural union.
The An-12 visited several major European cities, including Paris, Stockholm, Berlin, London, and Dusseldorf. It was used for commercial activities, transporting heavy cargo, mail, passengers, and animals. The aircraft remained in operation until July 1986, serving Bulgaria for 20 years. Notably, it is the only An-12 aircraft still in Bulgaria.
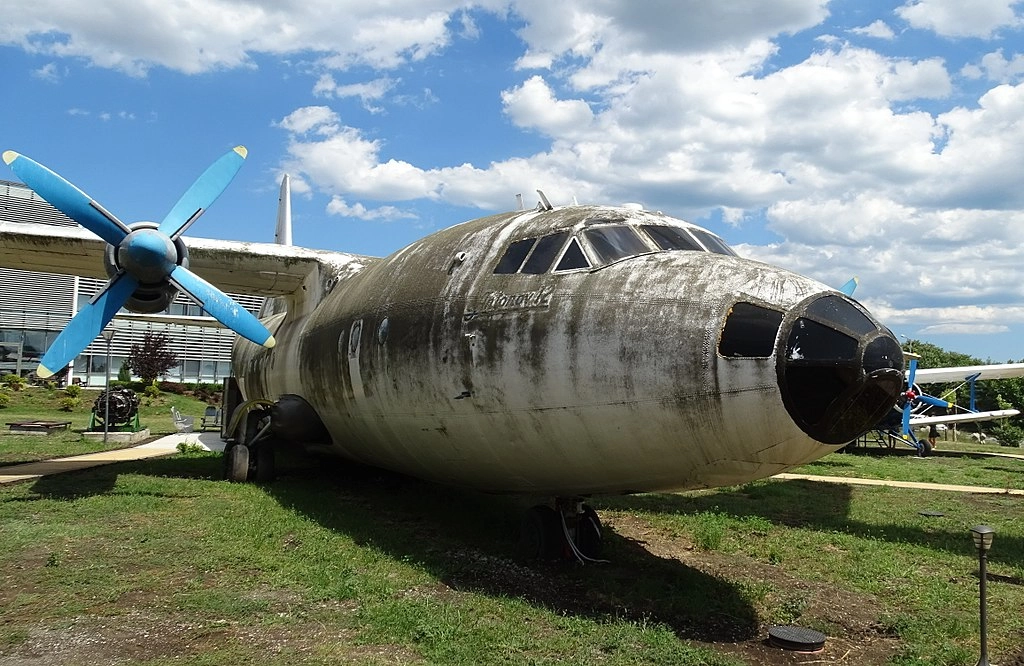

A total of 1,248 An-12 units were built, with the first flight taking place on December 16, 1957. The aircraft typically had a crew of 5 to 8 members, including two pilots, a flight engineer, a navigator, and a radio operator. It could carry 90 parachutists or 60 passengers. Currently, over 40 An-12 aircraft are still active across 7 countries.
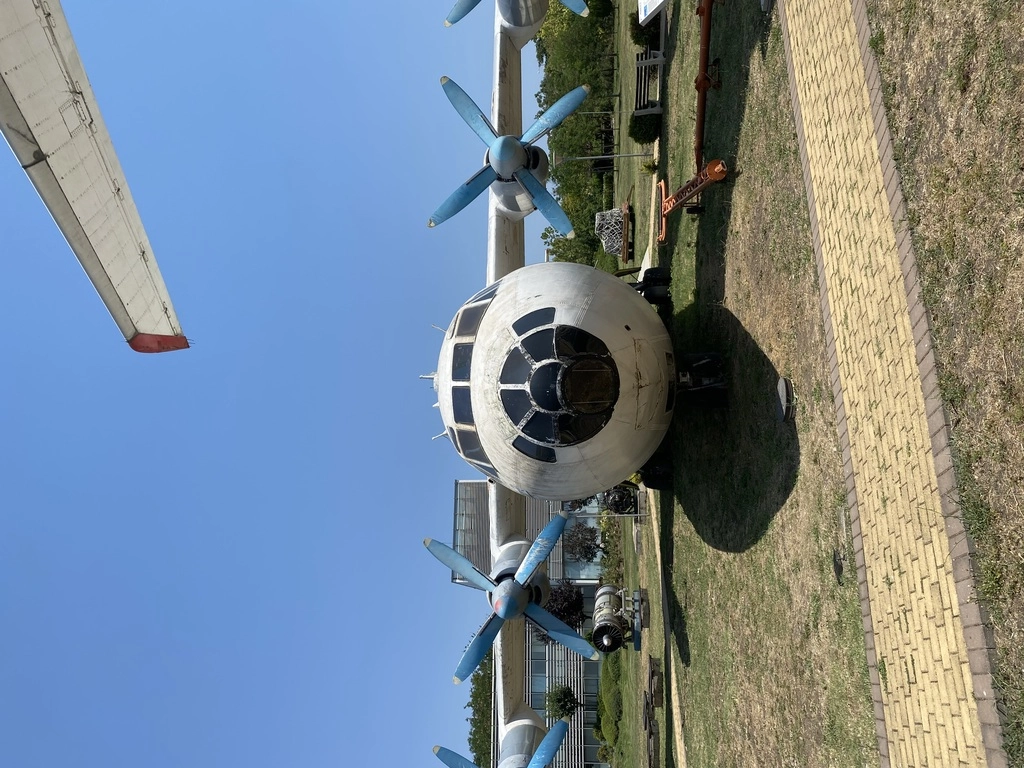

| AN-12 Specifications | Description |
|---|---|
| Length | 108 ft 7 in (33.1 m) |
| Wingspan | 124 ft 8 in (38 m) |
| Height | 34 ft 7 in (10.53 m) |
| Empty Weight | 61,729 lb (28,000 kg) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 134,482 lb (61,000 kg) |
| Engines | 4 × Ivchenko AI-20L or AI-20M |
| Engine Power | 4,023 hp |
| Cruise Speed | 350 mph (570 km/h) |
| Range | 3,100 nmi (5,700 km) |
| Service Ceiling | 33,500 ft (10,200 m) |

AN-24
The An-24 was produced and registered in 1976. This An-24 was used for transporting passengers. Its last flight occurred in August 1999, when it landed in Burgas, having served Bulgaria for 23 years.
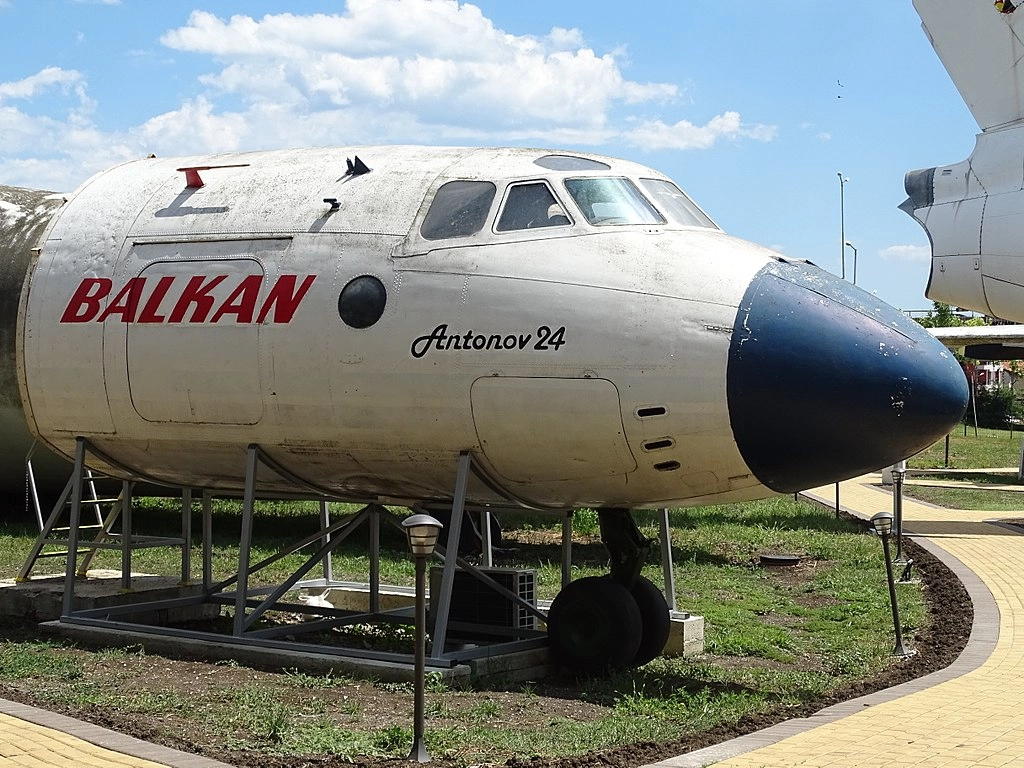

As of now, only Russia and Ukraine have 17 active AN-24 aircraft in their fleets. A total of 1,367 AN-24 units were built, with the first flight taking place on October 29, 1959. The aircraft typically operated with a crew of 3 members and could carry around 50 passengers.
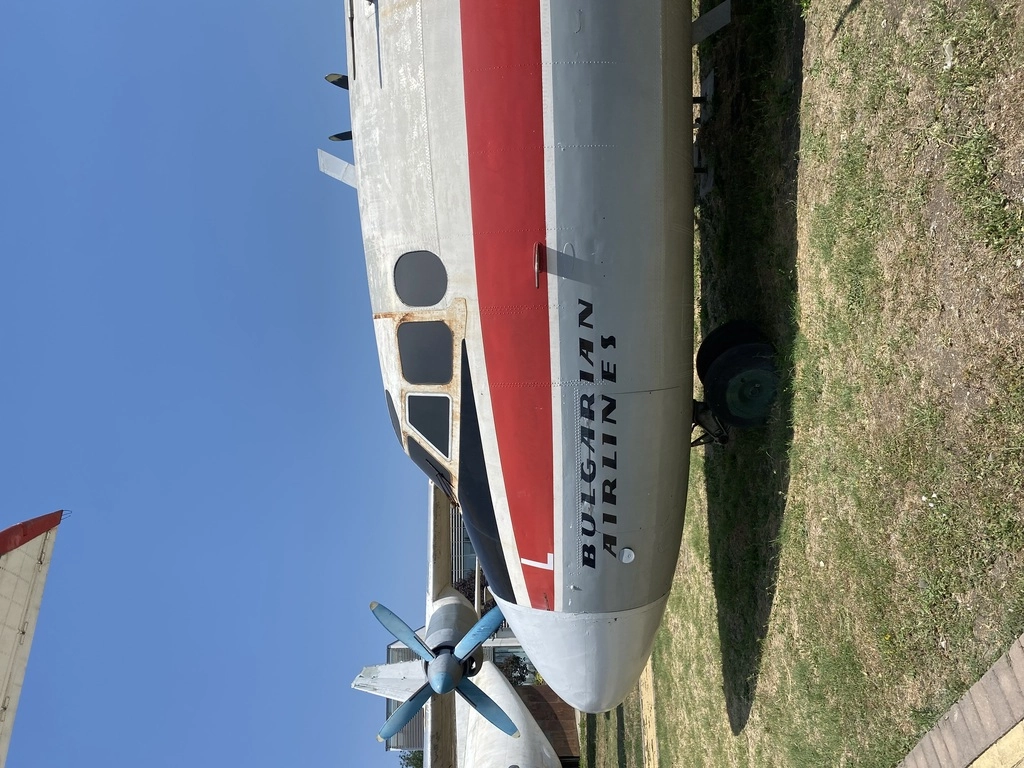

| AN-24 Specifications | Description |
|---|---|
| Length | 77 ft 2 in (23.53 m) |
| Wingspan | 95 ft 10 in (29.20 m) |
| Height | 27 ft 4 in (8.32 m) |
| Empty Weight | 29,321 lb (13,300 kg) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 46,297 lb (21,000 kg) |
| Engines | 2 × Ivchenko AI-20A |
| Engine Power | 2,547 hp |
| Cruise Speed | 280 mph (450 km/h) |
| Range | 1,300 nmi (2,400 km) |
| Service Ceiling | 27,600 ft (8,400 m) |

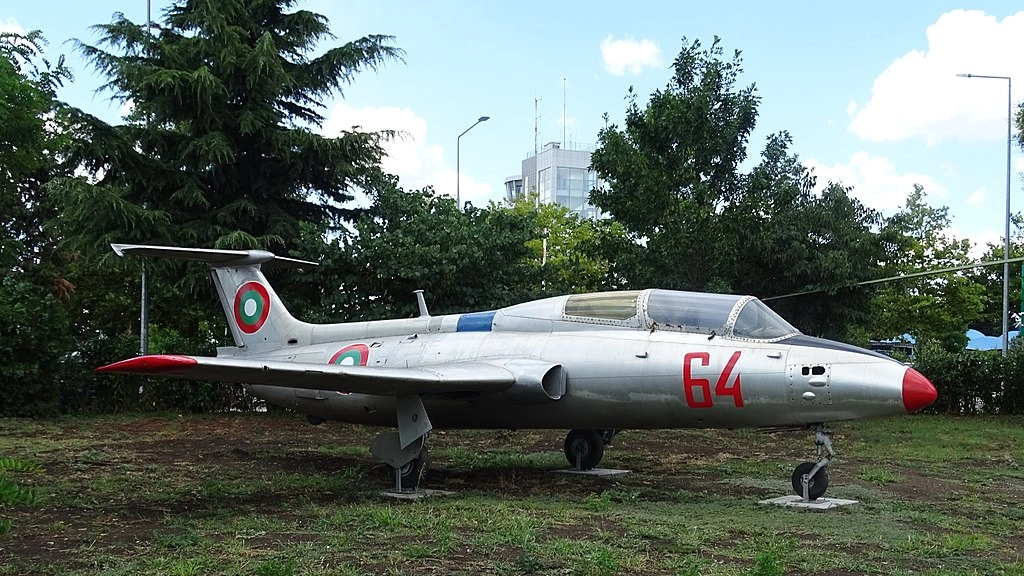
Aero L-29 Delfín
The L-29 is a light training aircraft capable of taking off and landing on grass, sand, and wet strips.
The L-29 marked the beginning of training for future jet pilots. This model was put into service in 1963, and the first aircraft arrived in Bulgaria in 1964.

The L-29 has a crew of 2 and its first flight was on April 5, 1959. Over a period of 12 years, 3,665 units were produced, demonstrating the aircraft’s robust design.
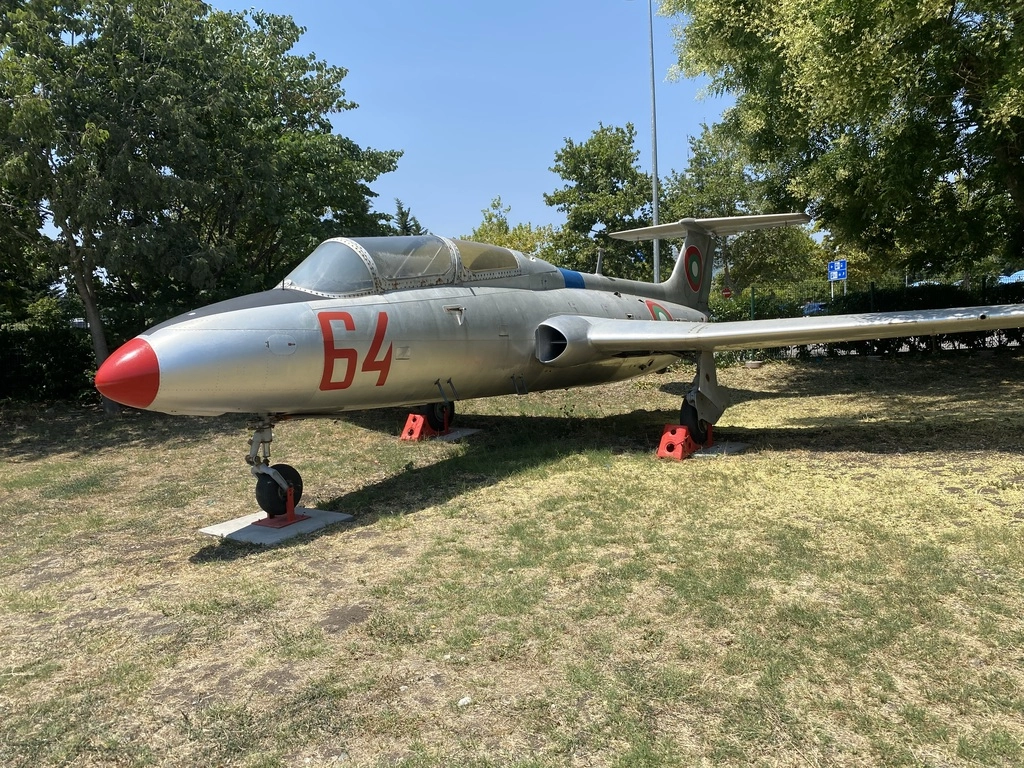

Currently, there are two military operators and more than five civilian operators owning some L-29 aircraft, although the exact number of operators and aircraft is unclear.
| L-29 Specifications | Description |
|---|---|
| Length | 35 ft 6 in (10.81 m) |
| Wingspan | 33 ft 9 in (10.29 m) |
| Height | 10 ft 3 in (3.13 m) |
| Empty Weight | 5,027 lb (2,280 kg) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 7,231 lb (3,280 kg) |
| Engines | 1 × Motorlet M-701c |
| Engine Power | 6,175 hp |
| Max Speed | 407 mph (655 km/h) |
| Range | 483 nmi (894 km) |
| Service Ceiling | 36,000 ft (11,000 m) |
Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-17
The MiG-17 is known for its excellent maneuverability and being the first Russian aircraft capable of near-supersonic speeds. Although it was not designed to be supersonic, skilled pilots could briefly reach supersonic speeds in a shallow dive.
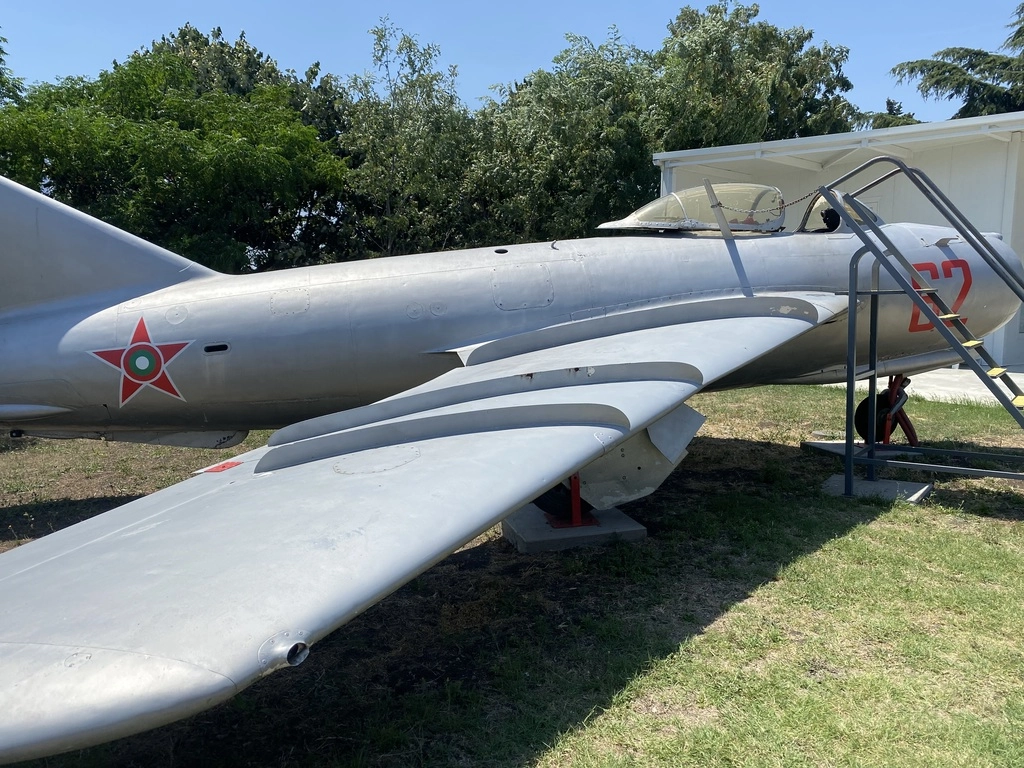

The MiG-17’s first flight took place on January 14, 1950, and a total of 10,649 units were built. It is operated by a single pilot. The North Korean Air Force still operates some of these aircraft, although the exact number is unknown.
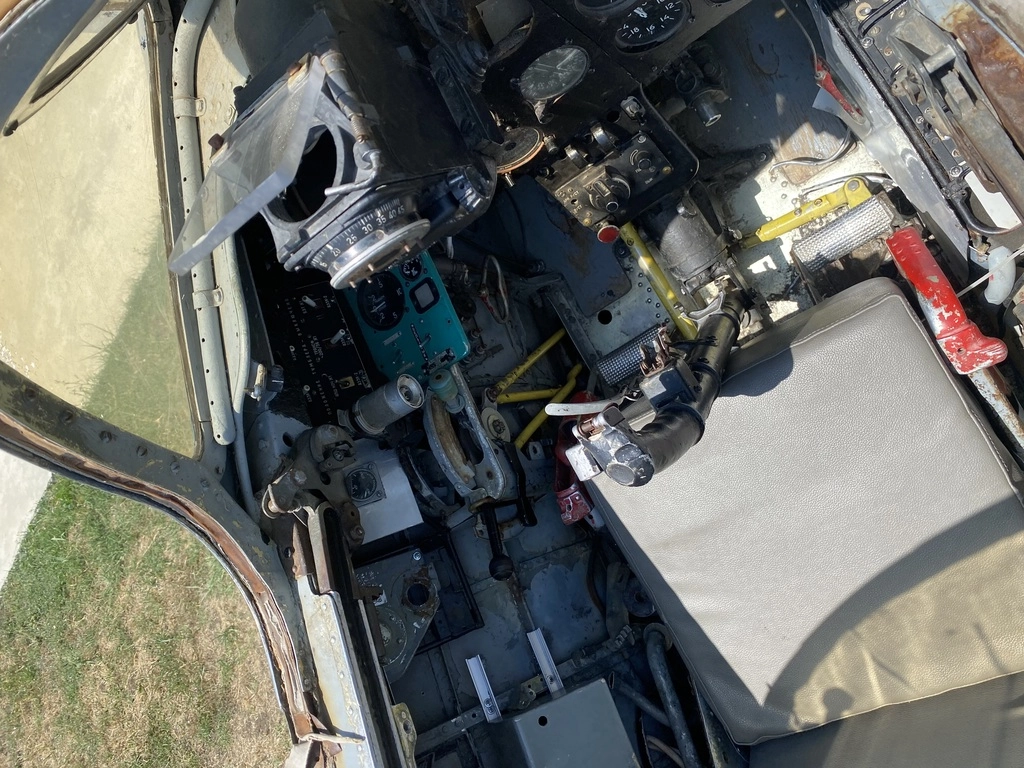

| MiG-17 Specifications | Description |
|---|---|
| Length | 36 ft 11 in (11.264 m) |
| Wingspan | 31 ft 7 in (9.628 m) |
| Height | 12 ft 6 in (3.8 m) |
| Empty Weight | 8,640 lb (3,919 kg) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 13,380 lb (6,069 kg) |
| Engines | 1 × Klimov VK-1F |
| Engine Power | 2,700 hp |
| Max Speed | 680 mph (1,100 km/h) |
| Range | 1,090 nmi (2,020 km) |
| Service Ceiling | 54,500 ft (16,600 m) |
Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21
This MiG-21 is a 1964 model and was in operation with Bulgaria for 52 years. It was decommissioned in August, 1995.
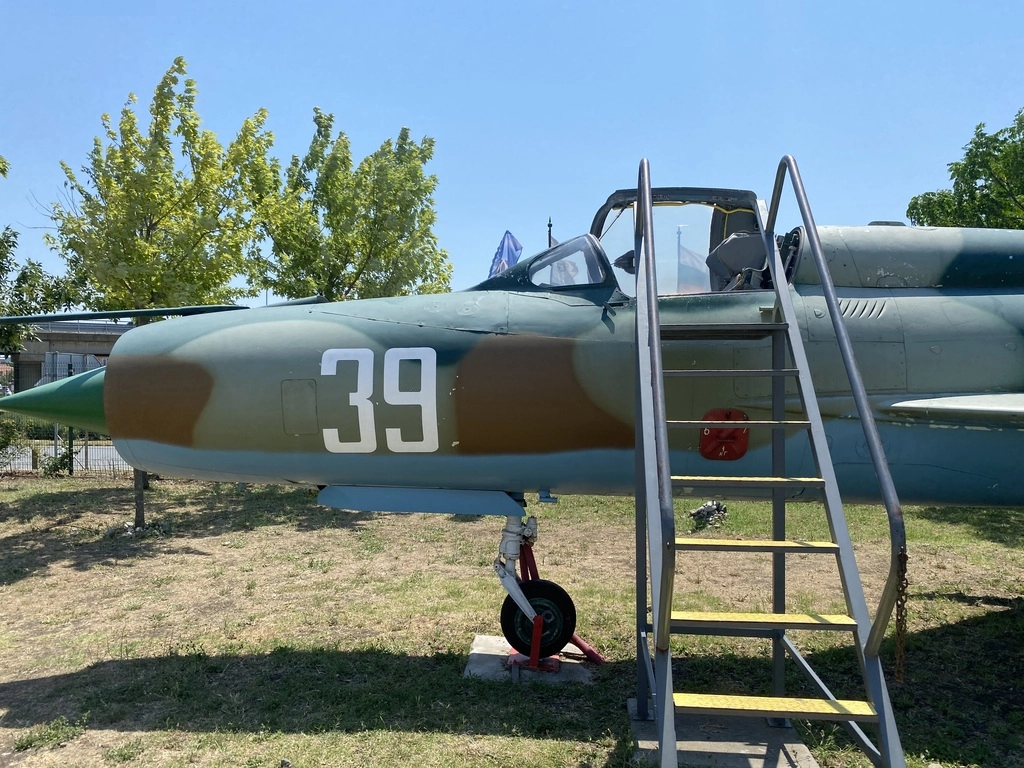

The MiG-21 is the most produced supersonic aircraft in history, with over 11,496 units built. It has been in service for more than 60 years across over 50 countries worldwide.
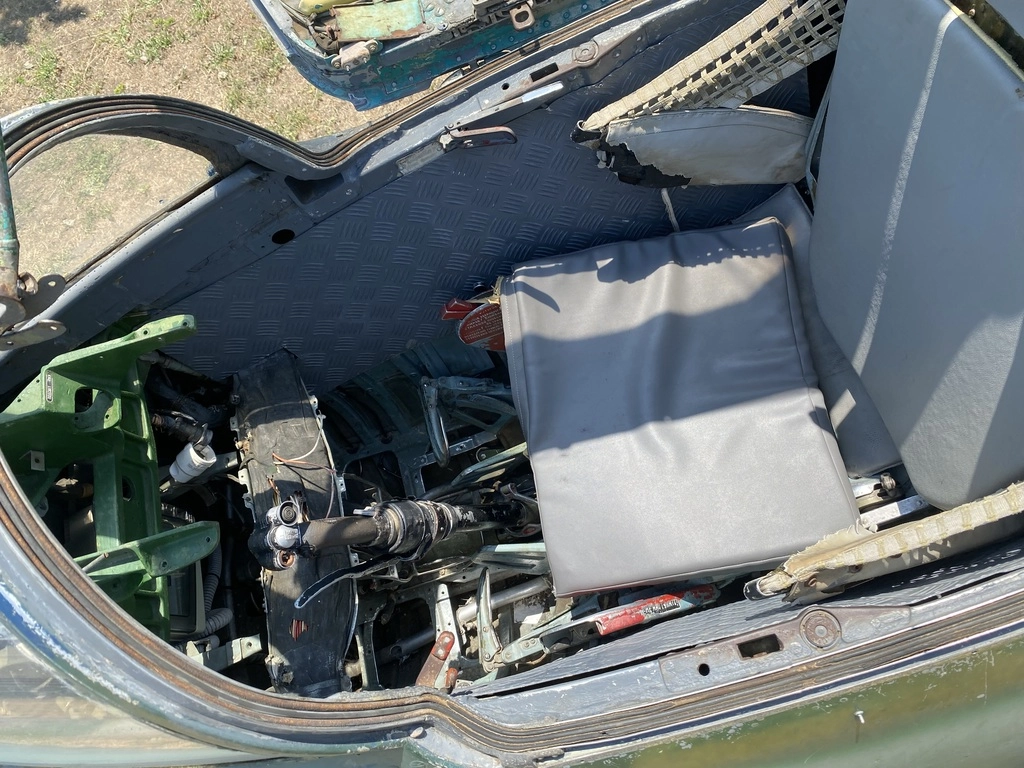

It had its first flight on June 16, 1955, and is operated by a single pilot. Many MiG-21 aircraft are still in service around the world today.

| MiG-21 Specifications | Description |
|---|---|
| Length | 48 ft 3 in (14.7 m) |
| Wingspan | 23 ft 6 in (7.154 m) |
| Height | 13 ft 5 in (4.1 m) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 19,401 lb (8,800 kg) |
| Engines | 1 × Tumansky R-25-300 |
| Engine Power | 6,175 hp |
| Max Speed | 1,351 mph (2,175 km/h) |
| Range | 360 nmi (660 km) |
| Service Ceiling | 57,400 ft (17,500 m) |
Mil Mi-2
One of the first helicopters registered in Bulgaria on June 30, 1973, the Mi-2 was used to monitor pollution in the Black Sea, fish movements, and marine conditions. Its last flight took place in September 1998 from Krumovo Air Base. The Mi-2 served Bulgaria for 25 years.
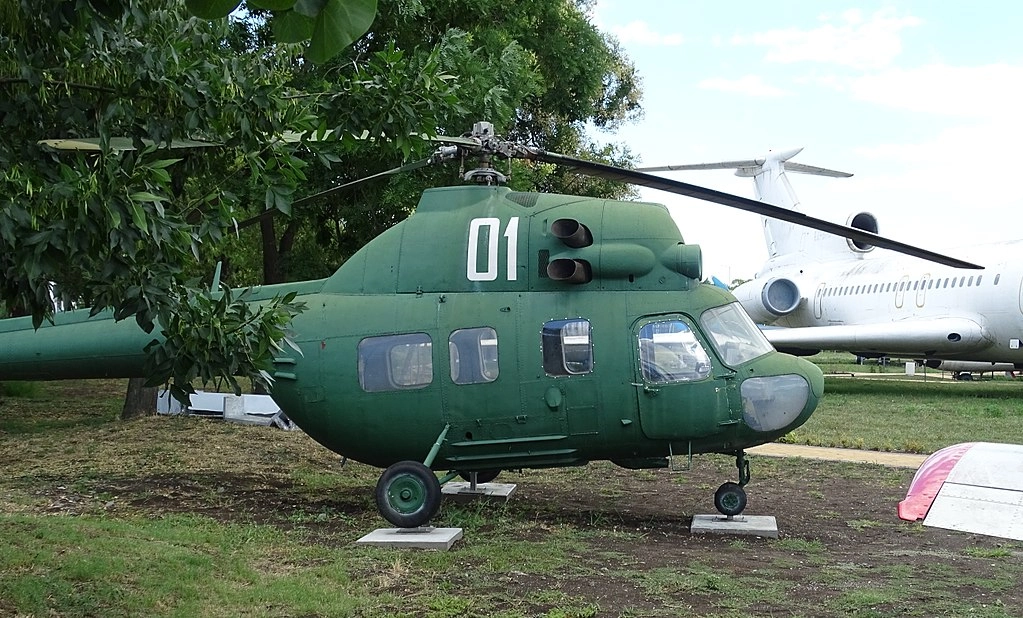

The Mi-2 had its first flight on September 22, 1961, and a total of 5,497 units were built. The helicopter is operated by one pilot and can carry up to 8 passengers. It is still in use in more than 15 countries.
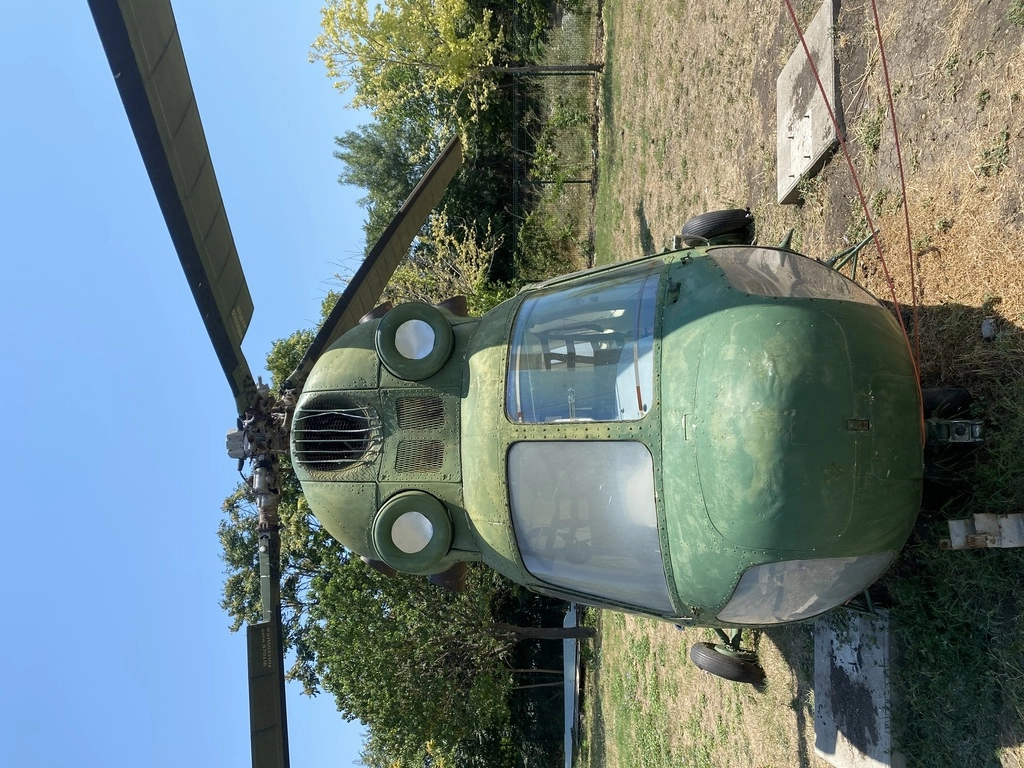

| MI-2 Specifications | Description |
|---|---|
| Length | 37 ft 5 in (11.4 m) |
| Height | 12 ft 4 in (3.75 m) |
| Empty Weight | 5,229 lb (2,372 kg) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 8,157 lb (3,700 kg) |
| Engines | 2 x GTD-350 |
| Engine Power | 2 x 298 hp |
| Max Speed | 120 mph (200 km/h) |
| Range with Max Fuel | 240 nmi (440 km) |
| Service Ceiling | 13,000 ft (4,000 m) |
Kamov Ka-26
The Soviet light utility helicopter, the Ka-26, had its first flight on August 18, 1965 and a total of 816 units were built.
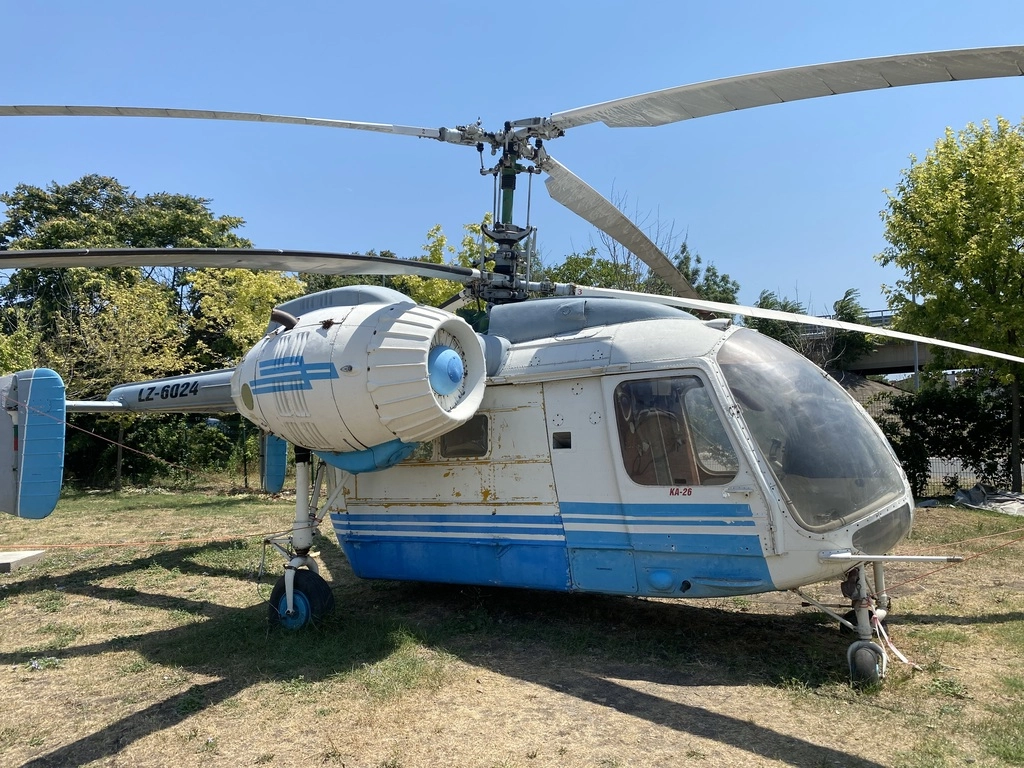

It typically operates with 1 or 2 crew members and can carry up to 7 passengers.
Currently, some Ka-26 helicopters remain active in Hungary, Russia, and Romania.
| KA-26 Specifications | Description |
|---|---|
| Length | 25 ft 5 in (7.75 m) |
| Width | 11 ft 11 in (3.64 m) |
| Height | 13 ft 3 in (4.05 m) |
| Empty Weight | 4,299 lb (1,950 kg) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 7,165 lb (3,250 kg) |
| Engines | 2 × Vedeneyev M-14V-26 9 |
| Engine Power | 2 x 325.2 hp |
| Cruise Speed | 93 mph (150 km/h) |
| Range | 220 nmi (400 km) |
| Service Ceiling | 9,800 ft (3,000 m) |