Note: I am, in no way shape or form, associated with Flighradar24.
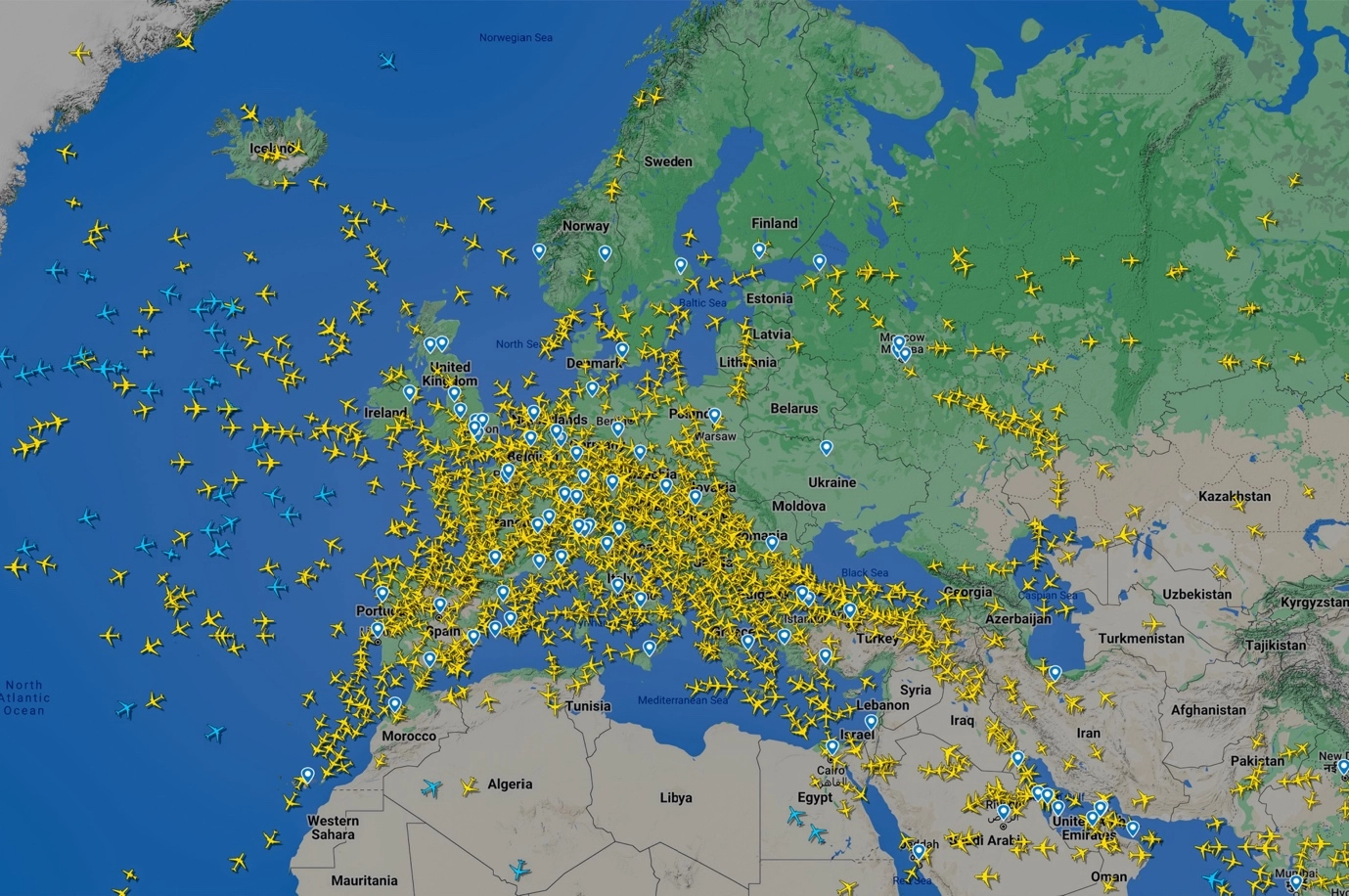
I am excited to introduce a remarkable real-time aircraft flight tracking website that I’ve been using since 2010. Not only is it user-friendly, but it also offers a wealth of valuable information.
In today’s fast-paced world, the ability to track flights in real-time has become an invaluable tool for aviation enthusiasts, travelers, and aviation professionals alike. Flightradar24, one of the most popular flight tracking services, has revolutionized the way we follow aircraft movements across the globe.
Therefore, this article will delve into the history of Flightradar24, explore how it works, and how to use it.
History of Flightradar24
Flightradar24 was founded in 2006 by Swedish aviation enthusiasts Fredrik Lindahl, Mikael Robertsson, and Olov Lindberg. The idea for the platform was born out of their passion for aviation and their desire to build a comprehensive flight tracking system that would provide real-time data on aircraft positions and flight details.
The platform encompasses a wide range of flight tracking data, such as flight details like origins and destinations, flight numbers, aircraft types, positions, altitudes, headings, and speeds. Moreover, it offers additional features like time-lapse replays of past flights and access to historical flight data categorized by airline, aircraft, aircraft type, geographic area, or airport.
When the service first opened in 2009 it relied on a network of volunteers who installed ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) receivers on their rooftops, allowing them to receive and share data from nearby aircraft. The information could also be received from satellite-based ADS-B receivers. Over time, the network expanded, covering more areas and improving the accuracy and coverage of the data.
In 2010, Flightradar24 gained significant exposure when international media relied on it to report the flight disruptions caused by the Eyjafjallajökull volcano eruptions over the North Atlantic and Europe.
Subsequently, starting from 3rd March 2020, the platform made ADS-B data collected by satellites accessible to all users. Aircraft located using satellite data were represented in blue on the map, while those located by terrestrial receivers appeared in yellow.
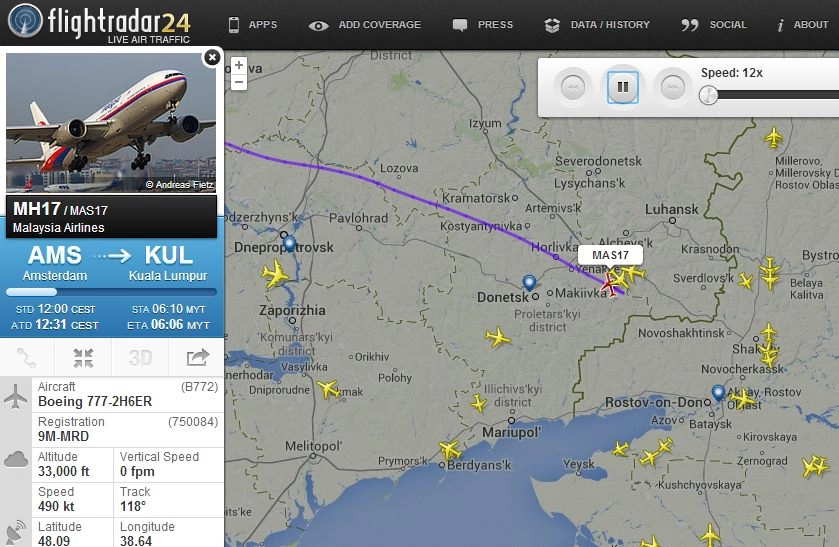
In February 2022, during the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the website experienced a crash due to a surge in visitors tracking flights in and around Ukraine.
How Flightradar24 Tracking Works
Flightradar24 employs a combination of ADS-B, MLAT (multilateration), satellites, FLARM (flight alarm), FAA (Federal Aviation Administration), and radar data to track flights worldwide. Here’s how it works:
ADS-B
ADS-B is a technology installed in modern aircraft that transmits real-time information, including the aircraft’s GPS-derived position, altitude, speed, heading, and identification code (ICAO24). The ADS-B signals are broadcast periodically and can be received by ground-based ADS-B receivers.
How does it work? The aircraft determines its location through a GPS navigation source, which utilizes satellite data. Meanwhile, the ADS-B transponder on the aircraft broadcasts a signal containing its location, along with additional information. This ADS-B signal is then received by a receiver linked to Flightradar24. The receiver feeds the acquired data to Flightradar24, where it is subsequently displayed on the website www.flightradar24.com and within the Flightradar24 apps.
ADS-B presents a significant advancement by replacing traditional radar technology with satellite-based tracking, offering substantial benefits. Unlike radar, which depends on radio signals and antennas to ascertain an aircraft’s position, ADS-B utilizes satellite signals for precise and efficient tracking of aircraft movements.
In 2019, approximately 80% of aircraft in Europe and 60% in the United States (US) were equipped with ADS-B technology. As of 2021, Flightradar24 boasts the largest ADS-B network globally, with over 30,000 connected receivers, making it a powerful and comprehensive flight-tracking service.
MLAT
In areas where ADS-B coverage is limited, Flightradar24 utilizes MLAT. MLAT is a technique that triangulates the aircraft’s position based on the time it takes for ADS-B signals to reach multiple receivers. By calculating the time difference, the system can estimate the aircraft’s location with high accuracy.
Although, there are some disadvantages. To accurately calculate the position of an aircraft, a minimum of four receivers is required. Also, while almost all of Europe enjoys comprehensive coverage, only certain areas in the US have the same level of coverage.
Radar Data
Flightradar24 also incorporates traditional radar data provided by various government agencies and air traffic control centers. Radar data is especially useful in regions where ADS-B coverage is minimal.
Satellites
Satellites equipped with ADS-B receivers gather data from aircraft in regions beyond the coverage of Flightradar24’s terrestrial ADS-B network and transmit this information to the Flightradar24 network.
FLARM
FLARM, a less complex variant of ADS-B with a limited range, is predominantly utilized by smaller aircraft, particularly gliders. The coverage of a FLARM receiver typically spans between 20 and 100 km.
FAA
To compensate for the coverage gap in the US, the FAA provides data with a delay of five minutes. However, this data might not include aircraft registration and other specific information.
Using Flightradar24
Using Flightradar24 is relatively straightforward, and it provides a wealth of information for aviation enthusiasts, travelers, and aviation professionals. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use Flightradar24 and how to interpret the data:
1. Accessing Flightradar24
Flightradar24 can be accessed through its website www.flightradar24.com or by downloading the Flightradar24 app from the respective app stores for iOS and Android devices.
2. Interface Overview
Once you access Flightradar24, you’ll be greeted with an interactive map interface displaying the world with various aircraft icons moving in real-time.
3. Aircraft Tracking
To track an aircraft, simply click on its icon on the map. A pop-up window will display detailed information about the flight, including flight number, aircraft type, altitude, speed, and departure and arrival airports.
4. Filtering Aircraft
Flightradar24 allows you to filter aircraft based on different criteria. You can choose to view specific airline flights, aircraft types, flight status (en route, landed, etc.), or limit the display to aircraft within a particular region.
5. Real-Time Data
The positions of aircraft on the map are updated in real-time, offering users the most current flight information.
6. Playback Feature
Flightradar24’s playback feature enables you to replay past flights and view historical data. You can select a specific date and time to see the positions and routes of flights that occurred in the past.
7. Aircraft Details
Clicking on an aircraft’s icon provides detailed information about the flight, such as the aircraft’s registration number, airline operator, flight path, and estimated arrival time.
8. Understanding Colors
Aircraft icons on the map may have different colors. Blue icons indicate aircraft whose positions are obtained from satellite-based ADS-B receivers, providing coverage in remote areas. Yellow icons represent aircraft tracked by terrestrial ADS-B receivers.
9. Weather Overlay
Flightradar24 allows users to overlay weather information on the map, including cloud cover, precipitation, and wind patterns, enabling a comprehensive view of flight conditions.
10. Safety Considerations
While Flightradar24 offers fascinating insights into the world of aviation, it is essential to remember that some aircraft may choose not to appear on the platform due to privacy or security concerns. Thus, not all flights may be visible.
Flightradar24 Subscription Plans
Although I have been using the Basic version throughout the years, I am now eager to show you all the available options and their respective features in-depth.
Basic (Free) Plan
The Basic plan was free of charge and provided users with limited access to real-time flight tracking features. Users could view live flights, aircraft positions, and basic flight information on the map.
Silver Plan
The Silver plan is a paid subscription that offers enhanced features beyond the Basic plan.
It provided users with additional flight tracking information, including weather overlays, extended historical flight data, and 90 days of flight history.
Gold Plan
The Gold plan is a more comprehensive subscription option with advanced functionalities.
In addition to all the features in the Silver plan, Gold subscribers gained access to a 365-day flight history and the ability to download historical data.
Business Plan
Flightradar24 also offers a Business plan designed for aviation professionals and enthusiasts requiring the most extensive data and coverage.
This plan is tailored to meet specific business needs and includes features such as airport view and AIRMETs/SIGMETs layer.
Future Developments
Since its inception, Flightradar24 has continually evolved and expanded its capabilities. The platform’s coverage and data accuracy have improved significantly, thanks to an ever-growing network of receivers and technological advancements. As technology continues to advance, we can expect Flightradar24 to further enhance its tracking capabilities and offer even more features and functionalities.
Sources: